Navigating the complex world of life insurance exams can be daunting, but with the right preparation, you can conquer these challenges and emerge victorious. This comprehensive guide, your ultimate “life insurance exam cheat sheet,” provides a clear roadmap to success, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies needed to ace your exam.
From understanding key concepts and exam structure to mastering effective study techniques and navigating ethical considerations, this guide covers all aspects of life insurance exams, leaving no stone unturned. Whether you’re a seasoned insurance professional or just starting your journey in the industry, this resource will serve as your trusted companion, empowering you to confidently face any life insurance exam.
Introduction to Life Insurance Exams
Life insurance exams are a crucial part of the process for obtaining life insurance coverage. They serve to assess the applicant’s health and determine the appropriate premium for the policy. The results of these exams help insurance companies assess the risk associated with insuring an individual.
These exams provide insurance companies with valuable information about the applicant’s overall health, which helps them make informed decisions about coverage and pricing.
Types of Life Insurance Exams
The type of life insurance exam required depends on the specific policy and the applicant’s circumstances. Here are the most common types:
- Paramedical Exam: This is the most common type of exam, involving a physical examination by a medical professional. The exam includes taking vital signs, measuring height and weight, and conducting basic medical tests such as blood and urine samples.
- Simplified Issue Life Insurance: This type of policy often requires a less extensive exam or may not require any exam at all. It is typically available for smaller coverage amounts and may have higher premiums.
- No Medical Exam Life Insurance: As the name suggests, this type of policy does not require a traditional medical exam. Instead, insurance companies rely on self-reported health information and may use other factors like age, health history, and lifestyle to assess risk.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Life insurance exams cover a range of key concepts and terminology related to health, risk assessment, and life insurance policies. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Underwriting: This process involves evaluating an applicant’s risk profile and determining whether to issue a policy and at what premium.
- Mortality Tables: These tables provide statistical data on life expectancy and death rates, which insurance companies use to calculate premiums.
- Premium: This is the regular payment an insured person makes to maintain their life insurance policy.
- Death Benefit: This is the lump sum payment made to the beneficiary upon the death of the insured person.
- Beneficiary: This is the individual or entity designated to receive the death benefit.
- Medical History: This includes information about past illnesses, surgeries, and medications.
- Lifestyle Factors: These include habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and exercise levels, which can influence risk assessment.
- Risk Factors: These are factors that can increase the likelihood of death or illness, such as age, family history, and medical conditions.
Key Concepts in Life Insurance
Life insurance is a financial contract that provides a death benefit to the beneficiary upon the death of the insured. This essential financial tool offers protection against financial hardship in the event of a loved one’s passing, ensuring their financial security and supporting their dependents. Understanding the various types of life insurance policies, their features, and the underlying concepts is crucial for making informed decisions about this important investment.
Types of Life Insurance Policies
Different types of life insurance policies cater to diverse needs and financial situations. Each policy type offers unique features and benefits, impacting the premiums, death benefit, and cash value.
- Term Life Insurance: This type of policy provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured dies within the term, the beneficiary receives the death benefit. Term life insurance offers affordable premiums, making it suitable for individuals with temporary needs, such as covering a mortgage or supporting children’s education. However, it does not accumulate cash value.
- Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage, guaranteeing a death benefit to the beneficiary regardless of when the insured passes away. It also accumulates cash value, which grows over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn. Whole life insurance premiums are typically higher than term life insurance, but it offers a combination of protection and investment.
- Universal Life Insurance: This flexible policy allows policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefit over time. Universal life insurance also accumulates cash value, which earns interest at a rate that can fluctuate. Policyholders have more control over their policy, but it can be complex and requires careful monitoring.
- Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance allows policyholders to invest their cash value in sub-accounts that fluctuate with the market. This provides the potential for higher returns but also carries greater risk. The death benefit can vary based on the performance of the investment sub-accounts.
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance: This type of policy combines features of universal life insurance with the potential for growth linked to a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. Policyholders benefit from potential market gains while enjoying the protection of a death benefit. However, the policy’s performance can be affected by market volatility.
Premiums
Premiums are the regular payments made by the policyholder to maintain the life insurance policy. They are calculated based on various factors, including the insured’s age, health, lifestyle, and the type of policy chosen.
Premiums are essentially the cost of the coverage provided by the life insurance policy.
Death Benefit
The death benefit is the lump-sum payment made to the beneficiary upon the insured’s death. It is the primary purpose of life insurance and is designed to provide financial security to the beneficiaries. The death benefit can be used to cover various expenses, such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and living expenses.
The death benefit is the core value of a life insurance policy, representing the financial protection it provides to the beneficiaries.
Cash Value
Some types of life insurance policies, such as whole life, universal life, and variable life, accumulate cash value. This component represents the policy’s savings component and grows over time. Policyholders can access the cash value through withdrawals, loans, or by surrendering the policy.
Cash value is an essential feature of certain life insurance policies, offering a combination of protection and investment.
Underwriting
Underwriting is the process of evaluating the risk associated with insuring an individual. Life insurance companies use underwriting to determine the policy’s premium, death benefit, and coverage terms. This involves assessing the insured’s health, lifestyle, occupation, and other factors that could impact their longevity.
Underwriting is a crucial step in the life insurance process, ensuring that premiums accurately reflect the risk involved.
Life Insurance Exam Structure
Life insurance exams are designed to assess your understanding of key concepts, principles, and regulations related to life insurance. The exam structure varies depending on the licensing body and the specific level of certification being pursued. However, there are common elements that are generally included in most life insurance exams.
Exam Structure
Life insurance exams typically consist of multiple-choice, true/false, and essay questions. The number of questions and the time allotted for the exam will vary depending on the exam level and licensing body. For instance, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) offers a series of exams, with each exam focusing on a specific area of insurance knowledge. The NAIC exams are designed to ensure that insurance professionals have the knowledge and skills necessary to provide quality service to their clients.
Types of Questions
- Multiple-Choice Questions: These questions present a statement or scenario followed by several possible answers. You must select the best answer from the choices provided. Multiple-choice questions are designed to test your understanding of basic concepts and definitions.
- True/False Questions: These questions present a statement, and you must determine whether the statement is true or false. True/false questions test your knowledge of specific facts and principles.
- Essay Questions: These questions require you to write a detailed response to a specific prompt. Essay questions are designed to assess your ability to apply your knowledge and understanding of life insurance concepts to real-world scenarios.
Examples of Exam Questions
- Multiple-Choice Question: Which of the following is NOT a type of life insurance policy?
- Term Life Insurance
- Whole Life Insurance
- Universal Life Insurance
- Health Insurance
- True/False Question: Life insurance premiums are typically higher for younger individuals.
- True
- False
- Essay Question: Explain the difference between term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
Exam Preparation Strategies

Passing a life insurance exam requires thorough preparation and a strategic approach. This section will Artikel effective study techniques, emphasizing the importance of reviewing relevant materials and recommending resources to aid in your preparation.
Reviewing Textbooks and Materials
Thorough review of textbooks and course materials is fundamental for success. These materials provide a comprehensive foundation for understanding life insurance concepts, regulations, and practices.
- Identify Key Concepts: Carefully review each chapter, focusing on key concepts, definitions, and formulas. Create flashcards or summaries to reinforce your understanding.
- Practice Problem Solving: Life insurance exams often include problem-solving questions. Work through practice problems in the textbook and use online resources to gain experience applying concepts.
- Seek Clarification: If you encounter any challenging concepts, don’t hesitate to seek clarification from instructors, study groups, or online forums.
Utilizing Practice Exams
Practice exams are essential for gauging your understanding and identifying areas that need further review. They simulate the actual exam environment, helping you become familiar with the format, question types, and time constraints.
- Identify Weaknesses: Practice exams help pinpoint areas where you need more focus. Analyze your performance to identify recurring errors or concepts you need to revisit.
- Develop Time Management Skills: Practice exams allow you to practice managing your time effectively during the actual exam. This is crucial for ensuring you complete all sections within the allotted time.
- Build Confidence: Regularly taking practice exams can boost your confidence by familiarizing you with the exam format and allowing you to experience success in a simulated setting.
Recommended Resources
Numerous resources can enhance your preparation. Beyond textbooks, consider exploring these options:
- Online Courses: Online courses offer structured learning experiences with interactive modules, quizzes, and practice exams. These courses can provide a comprehensive overview of life insurance concepts and exam-specific strategies.
- Study Guides: Study guides provide concise summaries of key concepts and exam-specific information. They can help you review material efficiently and identify areas requiring further study.
- Professional Organizations: Professional organizations like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) offer resources and study materials tailored to specific insurance exams.
Understanding Life Insurance Laws and Regulations
The life insurance industry operates within a complex legal and regulatory framework designed to protect policyholders and ensure the solvency of insurance companies. This section delves into the key legal and regulatory aspects that govern the life insurance industry.
Role of Insurance Commissioners and Regulatory Bodies
Insurance commissioners and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the life insurance industry. They are responsible for enforcing state and federal laws and regulations, ensuring the financial stability of insurance companies, and protecting policyholders from unfair or deceptive practices.
- State Insurance Commissioners: Each state has an insurance commissioner responsible for regulating the insurance industry within their jurisdiction. They issue licenses to insurance companies, monitor their financial health, and investigate consumer complaints.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization that provides a forum for state insurance regulators to share best practices and develop model laws and regulations. It plays a significant role in promoting uniformity and consistency in the regulation of insurance across states.
- Federal Regulators: The federal government also has a role in regulating the life insurance industry. For instance, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates the sale of variable life insurance products, and the Department of Labor (DOL) regulates employee benefit plans that include life insurance.
Common Life Insurance Laws and Regulations
Life insurance laws and regulations vary by state, but some common themes are found across jurisdictions. These laws address key areas such as:
- Licensing and Qualification: Insurance companies must be licensed to operate in a state and agents must be licensed to sell insurance products. Licensing requirements typically involve meeting certain financial and ethical standards.
- Financial Solvency: States require insurance companies to maintain adequate capital reserves to ensure they can meet their financial obligations to policyholders. This includes regular financial reporting and audits.
- Consumer Protection: Laws protect policyholders from unfair or deceptive practices, such as misrepresentation of policy terms or the use of high-pressure sales tactics. They also require insurance companies to provide clear and understandable policy disclosures.
- Policy Standards: States often set standards for the content and language of life insurance policies, including required disclosures and provisions related to policy ownership, beneficiaries, and death benefits.
- Regulation of Marketing and Sales Practices: Regulations govern the marketing and sale of life insurance products, including requirements for agent training, disclosure of policy features, and the use of illustrations.
Examples of Life Insurance Laws and Regulations
Here are some examples of specific life insurance laws and regulations that are commonly found in the United States:
- Unfair Trade Practices Act (UTPA): This law prohibits insurance companies from engaging in unfair or deceptive business practices. For example, it prohibits the use of misleading advertising or the misrepresentation of policy benefits.
- Life Insurance Guaranty Association (LIGA): These associations provide a safety net for policyholders in the event that an insurance company becomes insolvent. They typically guarantee the payment of death benefits up to a certain limit.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) Model Laws: The NAIC develops model laws and regulations that states can adopt to promote consistency and uniformity in the regulation of insurance. These model laws cover a wide range of areas, including licensing, solvency, and consumer protection.
Ethical Considerations in Life Insurance
The life insurance industry, like any other financial sector, operates within a framework of ethical principles that guide its practices and ensure the fair and transparent treatment of customers. These ethical considerations are crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the integrity of the industry.
Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency and disclosure are cornerstones of ethical conduct in the life insurance industry. This means that insurance professionals are obligated to be upfront and honest with customers about the terms and conditions of life insurance policies, including potential risks, exclusions, and limitations. Transparency is essential for informed decision-making by customers.
- Full Disclosure of Policy Details: Insurance agents and brokers must clearly explain the features, benefits, and limitations of each policy to potential customers. This includes outlining premiums, coverage amounts, waiting periods, exclusions, and any potential for policy lapses or cancellation.
- Accurate Representation of Products: Insurance professionals must present life insurance products truthfully and avoid misrepresenting their benefits or suitability for specific needs. They should ensure that customers understand the true nature of the product and its implications for their financial situation.
- Disclosure of Commissions and Fees: Transparency regarding commissions and fees earned by agents and brokers is crucial. Customers should be aware of any financial incentives that may influence the recommendations they receive.
Ethical Dilemmas and Challenges
Life insurance professionals face various ethical dilemmas and challenges in their daily practice. These situations require careful consideration and adherence to professional codes of conduct.
- Conflicts of Interest: Insurance professionals may face situations where their personal interests or affiliations could potentially compromise their objectivity when recommending life insurance products. This could include situations where they receive higher commissions for specific products or have relationships with certain insurance companies.
- Suitability of Products: Ensuring that life insurance products are suitable for individual customer needs is a critical ethical obligation. This involves considering factors like age, health, financial situation, and risk tolerance to determine the appropriate level of coverage and policy type.
- Misleading or Deceptive Sales Practices: Unethical sales practices can involve exaggerating the benefits of policies, downplaying potential risks, or using high-pressure tactics to persuade customers to purchase products that may not be in their best interests.
Life Insurance Industry Trends

The life insurance industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Understanding these trends is crucial for life insurance professionals to navigate the industry effectively and adapt to the changing landscape.
Impact of Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements are profoundly shaping the life insurance industry, impacting every aspect from product development to customer service.
- Digital Transformation: The industry is embracing digital platforms, mobile applications, and online portals to streamline operations, improve customer engagement, and enhance accessibility. This shift is leading to a more efficient and customer-centric approach to life insurance.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into various aspects of the life insurance value chain, including underwriting, risk assessment, and fraud detection. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and automate tasks, leading to more efficient and accurate decision-making.
- Data Analytics: The use of data analytics is transforming the industry, allowing insurers to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, market trends, and risk profiles. This data-driven approach enables insurers to develop personalized products and services, improve pricing strategies, and optimize risk management.
- Insurtech: The emergence of Insurtech startups is disrupting traditional insurance models by introducing innovative solutions and technologies. These startups are leveraging technology to offer more flexible, transparent, and personalized insurance products.
Future Outlook for the Life Insurance Industry
The life insurance industry is expected to continue evolving, driven by several key trends.
- Increased Demand for Life Insurance: Growing awareness of the importance of life insurance and the increasing need for financial protection are driving demand for life insurance products.
- Focus on Customer Experience: The industry is shifting its focus towards providing a seamless and personalized customer experience, leveraging digital technologies and data analytics to cater to individual needs.
- Rise of Digital Distribution Channels: The increasing adoption of digital platforms and online channels is changing the way life insurance is distributed. This shift is making life insurance more accessible and convenient for consumers.
- Emerging Products and Services: The industry is constantly innovating and developing new products and services to meet evolving customer needs. Examples include products tailored to specific demographics, such as millennials, and products that offer flexible coverage options and digital features.
Case Studies in Life Insurance
Life insurance case studies provide valuable insights into real-world scenarios, helping to understand the practical application of life insurance concepts and principles. These cases highlight the complexities, challenges, and potential outcomes associated with life insurance policies, enabling a deeper understanding of the industry and its impact on individuals and families.
Case Study: The Importance of Beneficiary Designation
This case study explores the critical importance of accurately designating beneficiaries for life insurance policies.
- Scenario: A married couple, John and Mary, had a life insurance policy on John’s life with Mary named as the beneficiary. After several years, John remarried, and he forgot to update the beneficiary designation on his life insurance policy. He passed away unexpectedly, leaving behind his new wife and two children from his previous marriage.
- Key Concepts:
- Beneficiary designation: The beneficiary is the individual(s) who will receive the death benefit upon the insured’s death.
- Importance of updating beneficiary designations: Life events such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of children can necessitate changes to beneficiary designations. Failure to update can result in unintended consequences, such as the death benefit being paid to the wrong person.
- Analysis:
- In this case, Mary, John’s first wife, received the entire death benefit despite John’s remarriage and subsequent children.
- This highlights the crucial need to review and update beneficiary designations periodically, especially when significant life events occur.
- Lessons Learned:
- Clearly and accurately designate beneficiaries on all life insurance policies.
- Review beneficiary designations regularly, especially after life events, to ensure they reflect your current wishes.
Life Insurance Exam Tips and Tricks

Passing a life insurance exam requires careful preparation and strategic test-taking techniques. This section provides practical tips and tricks to help you excel in your exam, manage exam anxiety, and optimize your performance.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Effective preparation is crucial for exam success. A structured approach can help you cover the necessary material and build confidence.
- Understand the Exam Syllabus: Begin by thoroughly reviewing the exam syllabus to identify the specific topics and learning objectives. This will help you prioritize your study efforts and focus on the most relevant areas.
- Develop a Study Plan: Create a realistic study schedule that allocates sufficient time for each topic. Break down large subjects into smaller, manageable chunks to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Utilize Various Learning Resources: Explore a variety of study materials, including textbooks, practice exams, online courses, and study guides. This multi-faceted approach can help you understand concepts from different perspectives and reinforce your knowledge.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice is essential for solidifying your understanding and improving your test-taking skills. Attempt practice exams, quizzes, and mock tests to familiarize yourself with the exam format and time constraints.
- Seek Clarification: If you encounter any concepts or questions that you find challenging, don’t hesitate to seek clarification from your instructors, study group members, or online forums.
Time Management and Effective Test-Taking
Effective time management and strategic test-taking techniques can significantly improve your exam performance.
- Pace Yourself: Allocate your time wisely by carefully reading each question and avoiding spending too much time on any single question. Move on to the next question if you get stuck and return to it later if time permits.
- Prioritize Easy Questions: Begin by answering the easier questions first to build momentum and confidence. This can help you save time for more challenging questions.
- Eliminate Incorrect Answers: For multiple-choice questions, use the process of elimination to narrow down the possible answers. This strategy can increase your chances of selecting the correct option.
- Read Carefully: Pay close attention to the wording of each question and answer choice. Look for s and qualifiers that can help you understand the intent of the question.
- Check Your Answers: If time allows, review your answers before submitting the exam. This step can help you catch any careless mistakes or oversights.
Managing Exam Anxiety and Stress
Exam anxiety is a common experience, but it can be managed with effective strategies.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to calm your nerves and reduce stress.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get sufficient sleep the night before the exam. A well-rested mind is better equipped to handle the pressure of the test.
- Eat a Healthy Meal: Avoid skipping meals or consuming sugary snacks before the exam. A healthy and balanced meal can provide sustained energy levels and help you focus.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated throughout the exam. Dehydration can lead to fatigue and decreased concentration.
- Positive Self-Talk: Engage in positive self-talk to boost your confidence and remind yourself of your preparation efforts.
Life Insurance Exam Resources

Preparing for a life insurance exam requires access to reliable and comprehensive resources. These resources can help you understand the complex concepts of life insurance, practice your knowledge, and gain confidence in your exam preparation.
Online Resources
Several online resources offer valuable information and practice materials for life insurance exams. These platforms provide a convenient and accessible way to study, allowing you to learn at your own pace.
- The American College of Financial Services: This organization offers various online courses, study materials, and practice exams for life insurance professionals. They provide a comprehensive approach to learning and prepare individuals for various licensing exams. Their website offers a vast library of resources, including articles, webinars, and downloadable materials.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a resource for state insurance regulators and provides information about insurance laws, regulations, and best practices. Their website offers a wealth of information on life insurance, including model laws, regulations, and exam preparation resources.
- Insurance Information Institute (III): The III is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing information about insurance to the public. Their website offers a variety of resources on life insurance, including articles, infographics, and videos. They also provide information about the insurance industry and its impact on society.
- Life Happens: Life Happens is a non-profit organization that provides information and resources about life insurance to consumers. Their website offers a variety of resources, including articles, calculators, and videos. They also provide information about the importance of life insurance and how to choose the right policy.
Textbooks and Study Guides
Textbooks and study guides provide a structured and in-depth approach to learning about life insurance. They offer comprehensive coverage of key concepts, laws, regulations, and industry practices.
- “Life Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide” by Robert B. Tuttle: This textbook offers a comprehensive overview of life insurance, covering its history, types, concepts, and applications. It includes detailed explanations of key terms, formulas, and industry practices.
- “The Life Insurance Exam Study Guide” by Kaplan: This study guide provides a focused approach to preparing for life insurance exams. It includes practice questions, test-taking strategies, and tips for success.
- “Life Insurance: A Practical Guide for Professionals” by The American College of Financial Services: This book provides a practical and comprehensive guide for life insurance professionals. It covers key concepts, laws, regulations, and industry best practices.
Professional Organizations and Support Groups
Professional organizations and support groups provide a platform for networking, professional development, and exam preparation. They offer resources, guidance, and a sense of community to individuals pursuing a career in life insurance.
- The National Association of Insurance and Financial Advisors (NAIFA): NAIFA is a professional association for insurance and financial advisors. They offer resources, education, and networking opportunities for individuals in the industry.
- The Society of Actuaries (SOA): The SOA is a professional organization for actuaries, who are professionals trained in the mathematics of insurance. They offer resources, education, and networking opportunities for actuaries.
- The American Society of Pension Professionals & Actuaries (ASPPA): ASPPA is a professional organization for professionals involved in retirement planning, employee benefits, and actuarial science. They offer resources, education, and networking opportunities for individuals in these fields.
Life Insurance Exam FAQs
Navigating the world of life insurance exams can be daunting, especially for those unfamiliar with the process. This section aims to address some of the most frequently asked questions about life insurance exams, offering clarity and alleviating any concerns you might have.
Exam Types and Formats
The type and format of a life insurance exam vary depending on the insurer and the specific policy being applied for. Here’s a breakdown of common exam types:
- Paramedical Exam: This is the most common type of life insurance exam. It involves a physical examination conducted by a qualified medical professional. The exam typically includes taking your vital signs (blood pressure, pulse, temperature), measuring your height and weight, and conducting a basic physical assessment. You may also be asked to provide a blood and urine sample for lab testing.
- Simplified Issue Life Insurance: Some insurers offer simplified issue life insurance policies that do not require a traditional medical exam. These policies often have lower coverage limits and may have higher premiums. The application process usually involves a health questionnaire and may include a review of your medical records.
- No Exam Life Insurance: Certain life insurance policies, often with lower coverage limits, require no medical exam at all. These policies are typically based on your self-reported health information and may have higher premiums than policies requiring a medical exam.
Exam Preparation and Tips
Preparing for a life insurance exam can help reduce anxiety and ensure a smooth experience. Here are some helpful tips:
- Understand the Exam Requirements: Before your exam, ensure you understand the specific requirements for your policy and the insurer. This includes the type of exam, any necessary paperwork, and any restrictions on food or drink before the exam.
- Be Honest and Transparent: Provide accurate and complete information about your medical history and current health status. Honesty is crucial to ensure you receive the right coverage and avoid potential complications later.
- Gather Necessary Documents: Prepare any relevant medical records, prescriptions, or other documentation that may be helpful for the exam. This can save time and ensure a more efficient process.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions if you are unsure about any aspect of the exam or the application process. The insurer’s representatives are there to assist you.
Exam Results and Appeal Process
Once you complete your life insurance exam, the insurer will review your medical information and determine your eligibility and premium.
- Understanding Your Results: The insurer will inform you of the results of your exam and the decision regarding your life insurance application. If approved, you will receive a policy with the agreed-upon coverage and premium.
- Appeal Process: If your application is denied or you are offered a policy with a higher premium than expected, you may have the right to appeal the decision. The appeal process involves providing additional information or evidence to support your case.
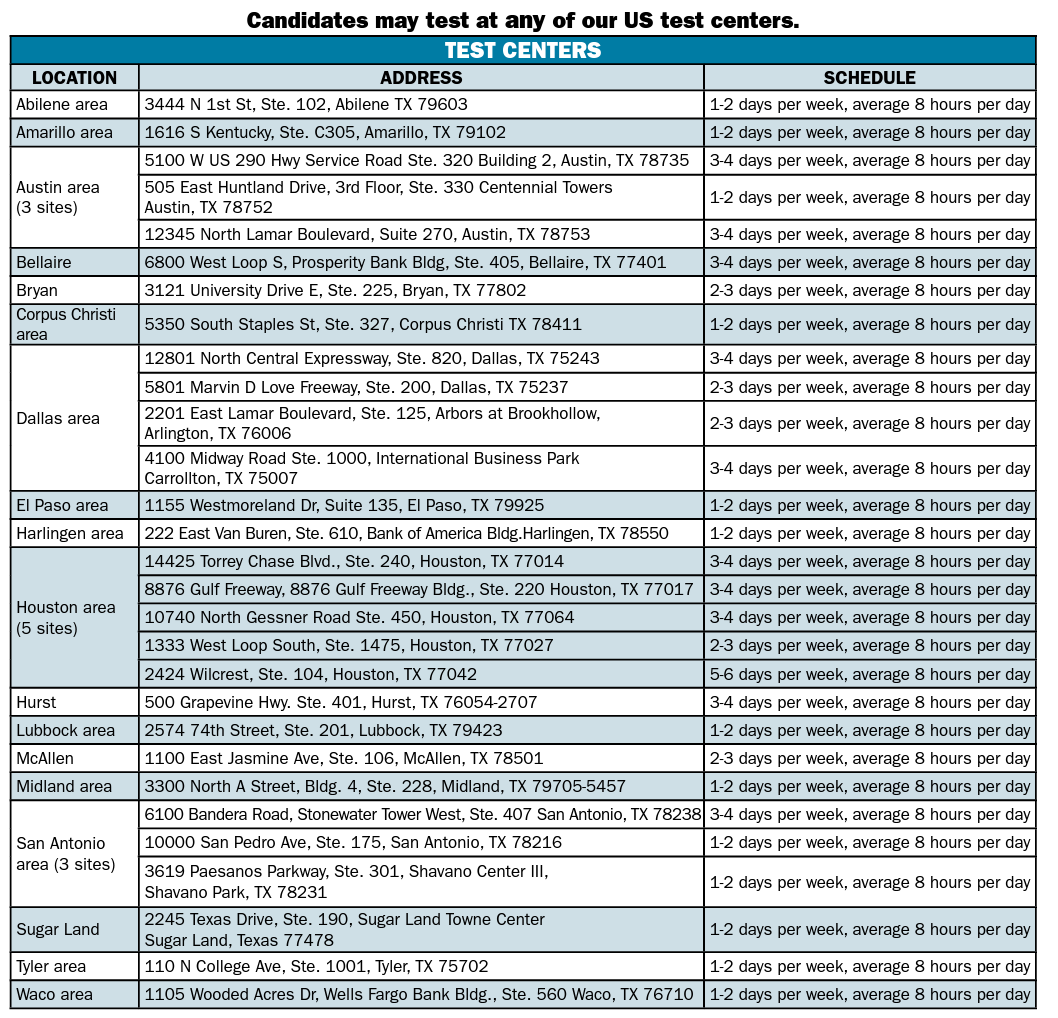
Final Review
As you embark on your journey to conquer the life insurance exam, remember that knowledge is power. Armed with this comprehensive cheat sheet, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the intricacies of life insurance, confidently answering questions and demonstrating your understanding of this crucial industry. Embrace the challenge, refine your skills, and emerge as a confident life insurance professional.






